By Jonathan Maresky, Product Marketing Manager, Cloudguard IaaS, published May 8th, 2019
VMware has been taking real action to back up CEO Pat Gelsinger’s assertion that hybrid-cloud is the new norm, most recently through updates to their NSX-T Data Center network virtualization platform for on-prem and cloud environments. NSX-T version 2.4 was a major milestone that saw the introduction of new advanced security capabilities.
Check Point was a design partner for the new version, which is fully supported by Check Point CloudGuard IaaS. This makes sense considering the close relationship between Check Point and VMware, and that CloudGuard was the first VMware partner product to be certified for NSX-T North/South service insertion.
(The supporting version of CloudGuard IaaS is currently in final stages of certification.)
Let’s dive into a few of the security enhancements in NSX-T version 2.4 and how CloudGuard IaaS uses them to harden private cloud security for Check Point customers.
Network Topology
CloudGuard supports NSX-T Inventory.
CloudGuard reads the inventory from NSX and allows the security operator to use objects from the inventory as part of the security policy. CloudGuard watches these objects and updates the gateway regarding any change that might occur on the NSX side.
NSX-T v2.4 allows the dynamic export of network topology, providing CloudGuard with immediate access to all network configuration changes.
Dynamic, Context-Based Grouping
NSX has rich contextual knowledge of the workloads it’s protecting. Instead of using grouping and rules based on where something is in the network, with NSX customers can use constructs based on specific characteristics of the workload, including for example the workload’s Operating System or name. By applying Security Tags, workloads can also be grouped based on criteria such as the function of the application, the application tier the workload is part of, the security posture, regulatory requirements or the environment the application is deployed in. Through the use of Security Tags, policies can be applied automatically to new workloads, thus reducing manual administrative overhead. For example, when you add a new VM: as soon as you apply a meaningful tag to the new VM, it automatically assumes the relevant policies of the tag’s groups.
You can also apply these policies automatically to new workloads, thus reducing manual administrative overhead.
For example, when you add a new VM: as soon as you apply a meaningful tag to the new VM, it automatically assumes the relevant policies of the tag’s groups.
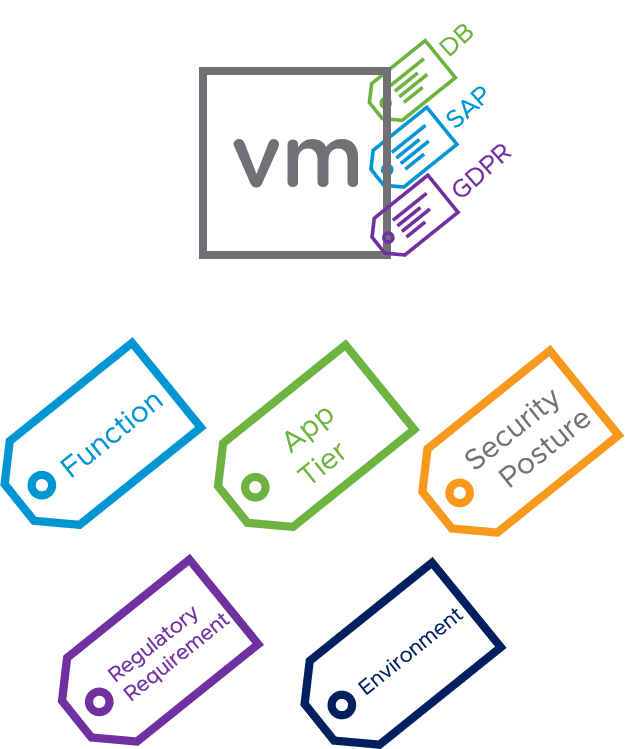
Applying Security Tags to a VM (source: VMware)
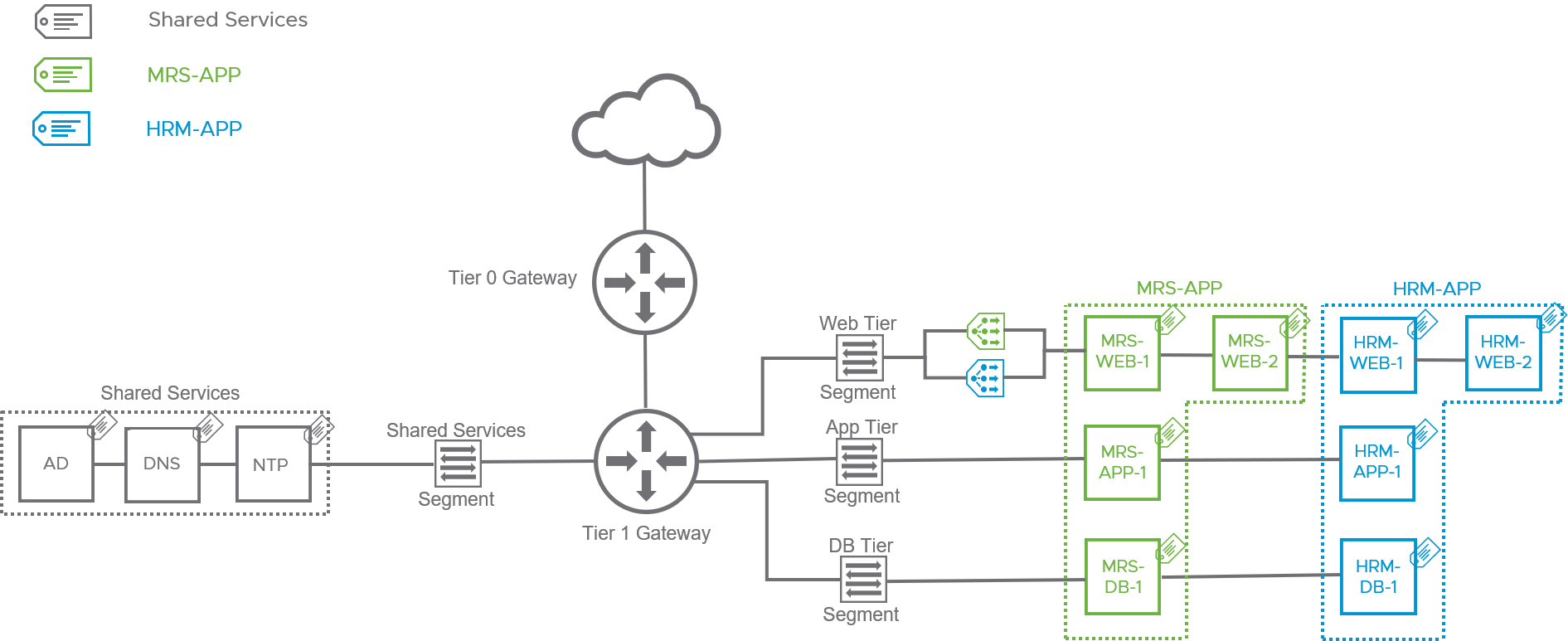
Example architecture with tags per application (source: VMware)
Policy-Based Service Insertion
Using VMware NSX-T and Check Point together provides strong security for North-South traffic entering the data center from the outside. This is done by connecting the CloudGuard IaaS security gateway to the T0-T1 router. NSX handles the deployment, plumbing and selective redirection of traffic to the CloudGuard IaaS security gateway.
CloudGuard IaaS provides powerful private cloud security features such as Firewall, Intrusion Prevention System, Anti-Bot, Antivirus, Application Control, and URL Filtering; as well as Threat Emulation and Threat Extraction for complete protection against the most sophisticated threats and zero-day vulnerabilities.
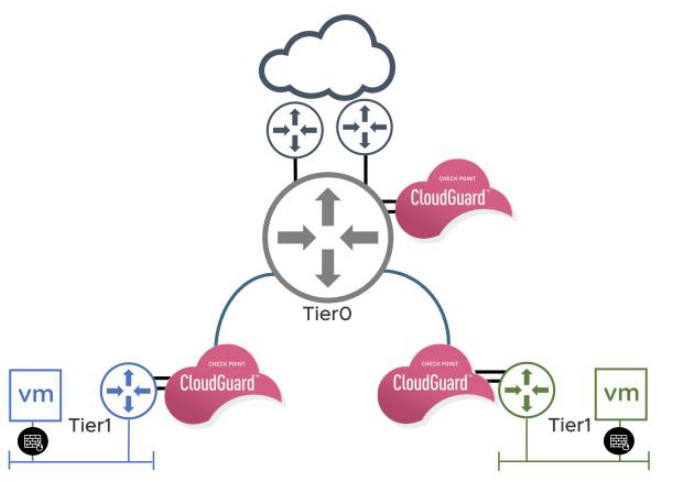
CloudGuard IaaS with N/S service insertion protects against advanced threats
But what about East-West traffic?
“Firewalls are conceptually sound, but execution often leaves network and security teams scrambling to patch flaws and fix mistakes that hackers have already discovered and exploited. Worse, once bad data packets such as malware enter into the network they may have unimpeded access to that “East-West” traffic inside the network.” (Pete Bartolik, CSO Online)
In other words, a breach of a single network can propagate across the data center, compromising all applications. Even attacks on low priority services can expose critical or sensitive systems.
With the Distributed Firewall, NSX-T enables micro-segmentation, enabling customers to provide granular firewalling for East-West traffic within the datacenter.
VMware NSX-T 2.4 introduces the enhancement of Policy-Based Service Insertion enabling partner solutions like Check Point CloudGuard to enhance the security of East-West traffic, without making changes in the topology.
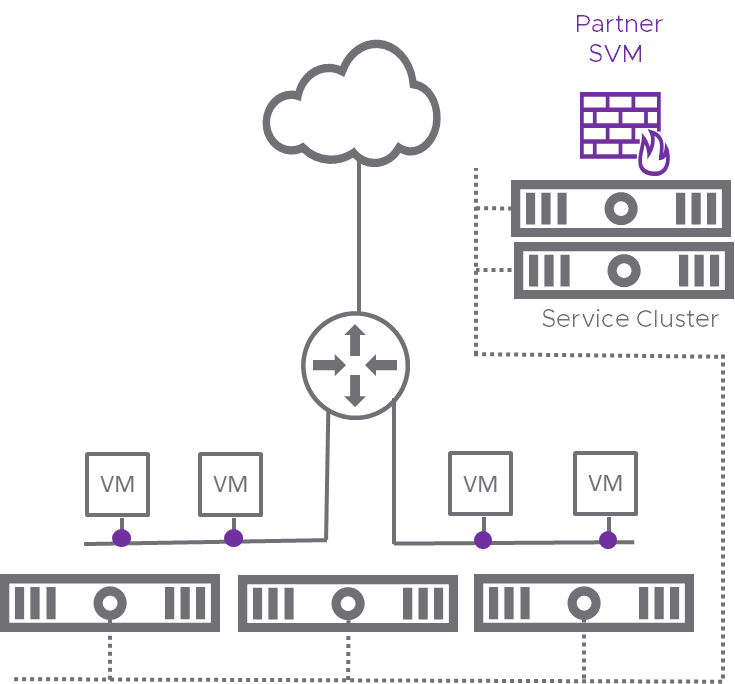
Policy-Based Service Insertion (source: VMware)
Checkpoint CloudGuard IaaS is integrating with NSX-T 2.4 East-West Service Insertion in order to provide robust protection of lateral traffic between different entities inside the cloud deployment. This lateral traffic may also be automatically redirected according to context-aware policies, as explained above.
The screenshot below shows the deployment of a new CloudGuard IaaS East-West service in the NSX-T Manager.
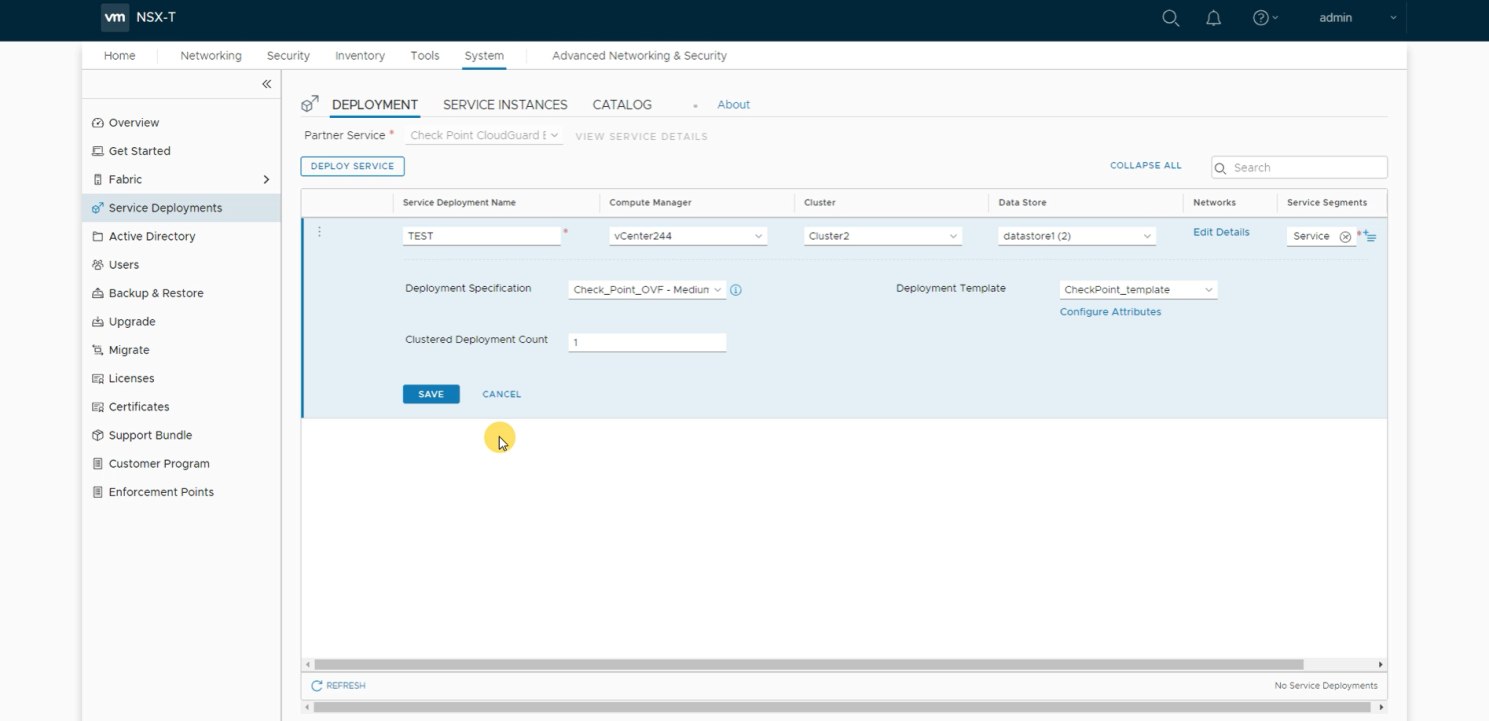
Deployment of a new CloudGuard IaaS East-West service in the NSX-T Manager
How Can You Improve Your Private Cloud Security?
Take precautions, including:
Check Point CloudGuard provides best-of-breed private cloud security, which is further enhanced by the above security enhancements introduced by VMware NSX-T 2.4.
CloudGuard provides consistent security policy enforcement and full threat visibility.
CloudGuard is well suited to dynamic multi-cloud and hybrid environments and supports the widest combination of private clouds and public clouds.
To learn more visit www.checkpoint.com.
The post Private Cloud Security: CloudGuard IaaS supports VMware’s new NSX-T 2.4 release appeared first on Check Point Software Blog.
from Check Point Software Blog http://bit.ly/2WCPwJf
via







 Jsecoin – JavaScript miner that can be embedded in websites. With JSEcoin, you can run the miner directly in your browser in exchange for an ad-free experience, in-game currency and other incentives.
Jsecoin – JavaScript miner that can be embedded in websites. With JSEcoin, you can run the miner directly in your browser in exchange for an ad-free experience, in-game currency and other incentives.
